Urinary Retention: What You Need to Know
Urinary retention means you can't fully empty your bladder when you pee. It might sound uncommon, but it affects many people at some point. It can be sudden and painful, or develop slowly and go unnoticed until it becomes serious. Knowing the causes and symptoms can help you spot trouble early and get the right treatment.
So, what causes urinary retention? It usually happens when something blocks the flow of urine or your bladder muscles aren't working right. In men, an enlarged prostate is a top cause. In both men and women, infections, certain medications, nerve problems, or muscle issues can play a role. Sometimes, injuries or surgeries around the urinary tract lead to retention too.
Spotting the Signs
How do you know if you have urinary retention? You might feel the urge to urinate but struggle to start peeing or take a very weak, slow stream. Some people notice their bladder feels full all the time or experience frequent trips to the bathroom with little output. Pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen can also be a clue. If these happen suddenly, it’s important to get help fast because acute retention can be pretty painful and even harmful.
Treatment Options That Work
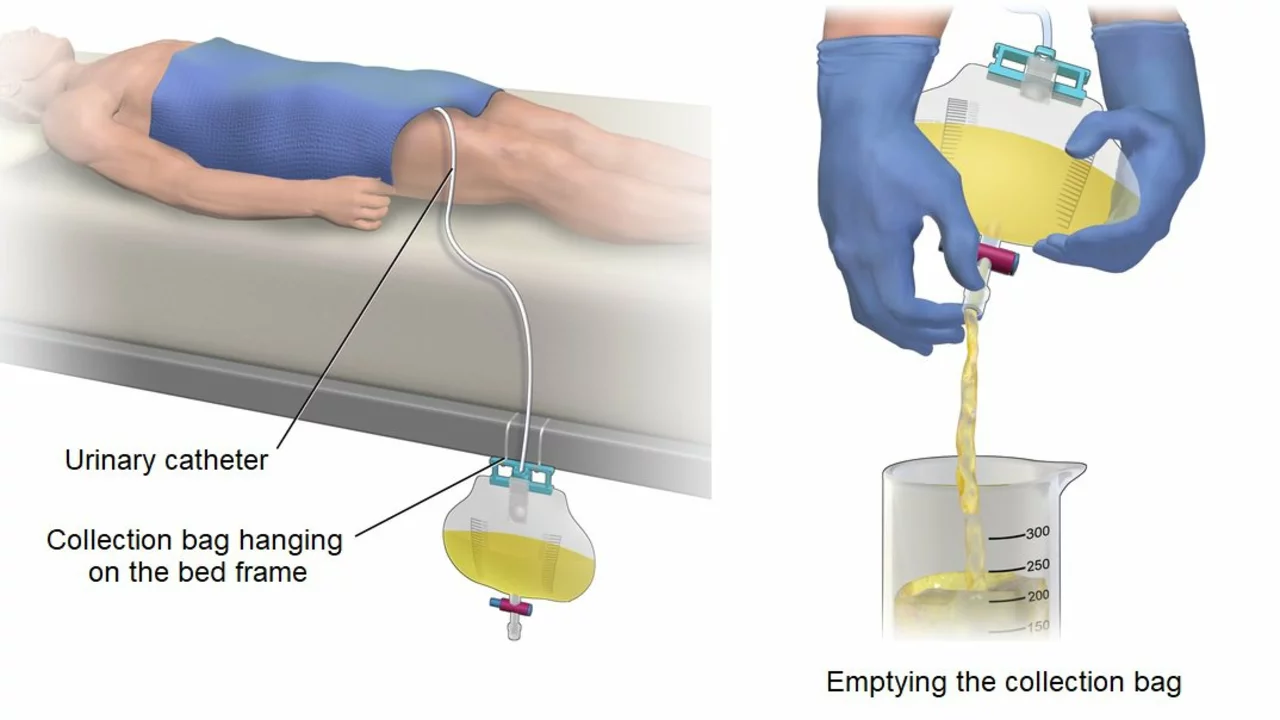
Treatment depends on what’s causing the problem. Doctors may temporarily relieve it by using a catheter to drain your bladder. For longer-term fixes, they tackle the root cause. If an enlarged prostate is the issue, medications or surgery might be recommended. Infections need antibiotics, while other causes like nerve problems may need specialized care. Lifestyle changes such as staying hydrated, avoiding alcohol and caffeine, or timed voiding can also help manage symptoms.
Don’t ignore urinary retention or assume it will go away. Left untreated, it can lead to infections, bladder damage, or kidney problems. If peeing feels off or you find yourself straining often, check in with a healthcare provider. Quick action and proper treatment can save you a lot of discomfort and keep your urinary system healthy.
Published on Apr 29
19 Comments
As a blogger, I have recently explored the topic of Imipramine and urinary retention. Imipramine is an antidepressant medication that, although effective, can sometimes lead to urinary retention - an uncomfortable and potentially dangerous side effect. To treat this problem, doctors may prescribe alternative medications, adjust dosages, or recommend non-pharmacological interventions. In addition, I've discovered some helpful prevention tips, such as staying hydrated, practicing bladder training, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Overall, understanding the causes and management options for Imipramine-related urinary retention is essential for those taking this medication.